-
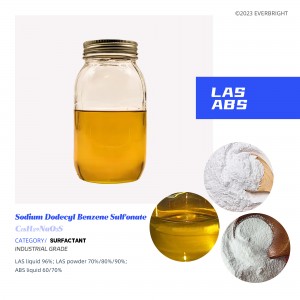
Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate (SDBS/LAS/ABS)
It is a commonly used anionic surfactant, which is a white or light yellow powder/flake solid or brown viscous liquid, difficult to volatilization, easy to dissolve in water, with branched chain structure (ABS) and straight chain structure (LAS), the branched chain structure is small in biodegradability, will cause pollution to the environment, and the straight chain structure is easy to biodegrade, the biodegradability can be greater than 90%, and the degree of environmental pollution is small.
-

Dodecylbenzenesulphonic acid (DBAS/LAS/LABS)
Dodecyl benzene is obtained by condensation of chloroalkyl or α-olefin with benzene. Dodecyl benzene is sulfonated with sulfur trioxide or fuming sulfuric acid. Light yellow to brown viscous liquid, soluble in water, hot when diluted with water. Slightly soluble in benzene, xylene, soluble in methanol, ethanol, propyl alcohol, ether and other organic solvents. It has the functions of emulsification, dispersion and decontamination.
-

Sodium Sulfate
Sodium sulfate is sulfate and sodium ion synthesis of salt, sodium sulfate soluble in water, its solution is mostly neutral, soluble in glycerol but not soluble in ethanol. Inorganic compounds, high purity, fine particles of anhydrous matter called sodium powder. White, odorless, bitter, hygroscopic. The shape is colorless, transparent, large crystals or small granular crystals. Sodium sulfate is easy to absorb water when exposed to air, resulting in sodium sulfate decahydrate, also known as glauborite, which is alkaline.
-

Sodium Peroxyborate
Sodium perborate is an inorganic compound, white granular powder. Soluble in acid, alkali and glycerin, slightly soluble in water, mainly used as oxidant, disinfectant, fungicide, mordant, deodorant, plating solution additives, etc. Mainly used as oxidant, disinfectant, fungicide, mordant, deodorant, plating solution additive and so on.
-

Sodium Percarbonate(SPC)
Sodium percarbonate appearance is white, loose, good fluidity granular or powdery solid, odorless, easily soluble in water, also known as sodium bicarbonate. A solid powder. It is hygroscopic. Stable when dry. It slowly breaks down in the air to form carbon dioxide and oxygen. It quickly breaks down into sodium bicarbonate and oxygen in water. It decomposes in dilute sulfuric acid to produce quantifiable hydrogen peroxide. It can be prepared by the reaction of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide. Used as an oxidizing agent.
-

Alkaline Protease
The main source is microbial extraction, and the most studied and applied bacteria are mainly Bacillus, with subtilis as the most, and there are also a small number of other bacteria, such as Streptomyces. Stable at pH6 ~ 10, less than 6 or more than 11 quickly deactivated. Its active center contains serine, so it is called serine protease. Widely used in detergent, food, medical, brewing, silk, leather and other industries.
-

Sodium Tripolyphosphate(STPP)
Sodium tripolyphosphate is an inorganic compound containing three phosphate hydroxyl groups (PO3H) and two phosphate hydroxyl groups (PO4). It is white or yellowish, bitter, soluble in water, alkaline in aqueous solution, and releases a lot of heat when dissolved in acid and ammonium sulfate. At high temperatures, it breaks down into products such as sodium hypophosphite (Na2HPO4) and sodium phosphite (NaPO3).
-

Carboxymethyl Cellulose(CMC)
At present, the modification technology of cellulose mainly focuses on etherification and esterification. Carboxymethylation is a kind of etherification technology. Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) is obtained by carboxymethylation of cellulose, and its aqueous solution has the functions of thickening, film formation, bonding, moisture retention, colloidal protection, emulsification and suspension, and is widely used in washing, petroleum, food, medicine, textile and paper and other industries. It is one of the most important cellulose ethers.
-

4A Zeolite
It is a natural alumino-silicic acid, salt ore in the burning, due to the water inside the crystal is driven out, producing a phenomenon similar to bubbling and boiling, which is called “boiling stone” in image, referred to as “zeolite”, used as a phosphate-free detergent auxiliary, instead of sodium tripolyphosphate; In the petroleum and other industries, it is used as a drying, dehydration and purification of gases and liquids, and also as a catalyst and water softener.
-

Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate
One of the sodium salts of phosphoric acid, an inorganic acid salt, soluble in water, almost insoluble in ethanol. Sodium dihydrogen phosphate is a raw material for the manufacture of sodium hempetaphosphate and sodium pyrophosphate. It is colorless transparent monoclinic prismatic crystal with a relative density of 1.52g/cm².
-

CAB-35 (Cocoamidopropyl Betaine)
Cocamidopropyl betaine was prepared from coconut oil by condensation with N and N dimethylpropylenediamine and quaternization with sodium chloroacetate (monochloroacetic acid and sodium carbonate). The yield was about 90%. It is widely used in the preparation of middle and high grade shampoo, body wash, hand sanitizer, foaming cleanser and household detergent.
-

Dibasic Sodium Phosphate
It is one of the sodium salts of phosphoric acid. It is a deliquescent white powder, soluble in water, and the aqueous solution is weakly alkaline. Disodium hydrogen phosphate is easy to weather in the air, at room temperature placed in the air to lose about 5 crystal water to form heptahydrate, heated to 100℃ to lose all the crystal water into anhydrous matter, decomposition into sodium pyrophosphate at 250℃.