-

Dibasic Sodium Phosphate
It is one of the sodium salts of phosphoric acid. It is a deliquescent white powder, soluble in water, and the aqueous solution is weakly alkaline. Disodium hydrogen phosphate is easy to weather in the air, at room temperature placed in the air to lose about 5 crystal water to form heptahydrate, heated to 100℃ to lose all the crystal water into anhydrous matter, decomposition into sodium pyrophosphate at 250℃.
-

Polyaluminum Chloride liquid (Pac)
Polyaluminum chloride is an inorganic substance, a new water purification material, inorganic polymer coagulant, referred to as polyaluminum. It is a water-soluble inorganic polymer between AlCl3 and Al(OH)3, which has a high degree of electric neutralization and bridging effect on colloids and particles in water, and can strongly remove micro-toxic substances and heavy metal ions, and has stable properties.
-

Citric Acid
It is an important organic acid, colorless crystal, odorless, has a strong sour taste, easily soluble in water, mainly used in food and beverage industry, can be used as sour agent, seasoning agent and preservative, preservative, can also be used in chemical, cosmetic industry as an antioxidant, plasticizer, detergent, anhydrous citric acid can also be used in food and beverage industry.
-

CAB-35 (Cocoamidopropyl Betaine)
Cocamidopropyl betaine was prepared from coconut oil by condensation with N and N dimethylpropylenediamine and quaternization with sodium chloroacetate (monochloroacetic acid and sodium carbonate). The yield was about 90%. It is widely used in the preparation of middle and high grade shampoo, body wash, hand sanitizer, foaming cleanser and household detergent.
-

Sodium Chloride
Its source is mainly seawater, which is the main component of salt. Soluble in water, glycerin, slightly soluble in ethanol (alcohol), liquid ammonia; Insoluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid. Impure sodium chloride is deliquescent in air. The stability is relatively good, its aqueous solution is neutral, and the industry generally uses the method of electrolytic saturated sodium chloride solution to produce hydrogen, chlorine and caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) and other chemical products (generally known as chlor-alkali industry) can also be used for ore smelting (electrolytic molten sodium chloride crystals to produce active sodium metal).
-

Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate
One of the sodium salts of phosphoric acid, an inorganic acid salt, soluble in water, almost insoluble in ethanol. Sodium dihydrogen phosphate is a raw material for the manufacture of sodium hempetaphosphate and sodium pyrophosphate. It is colorless transparent monoclinic prismatic crystal with a relative density of 1.52g/cm².
-

Boric Acid
It is a white crystalline powder, with a smooth feel and no odor. Its acidic source is not to give protons by itself. Because boron is an electron deficient atom, it can add hydroxide ions of water molecules and release protons. Taking advantage of this electron-deficient property, polyhydroxyl compounds (such as glycerol and glycerol, etc.) are added to form stable complexes to strengthen their acidity.
-

CDEA 6501/6501h (Coconutt Diethanol Amide)
CDEA can enhance the cleaning effect, can be used as an additive, foam stabilizer, foam aid, mainly used in the manufacture of shampoo and liquid detergent. An opaque mist solution is formed in water, which can be completely transparent under a certain agitation, and can be completely dissolved in different kinds of surfactants at a certain concentration, and can also be completely dissolved in low carbon and high carbon.
-

Ammonium Sulfate
An inorganic substance, colorless crystals or white particles, odorless. Decomposition above 280℃. Solubility in water: 70.6g at 0℃, 103.8g at 100℃. Insoluble in ethanol and acetone. A 0.1mol/L aqueous solution has a pH of 5.5. The relative density is 1.77. Refractive index 1.521.
-

Hydrofluoric Acid (HF)
It is an aqueous solution of hydrogen fluoride gas, which is a transparent, colorless, smoking corrosive liquid with a strong pungent odor. Hydrofluoric acid is an extremely corrosive weak acid, which is highly corrosive to metal, glass and silicon-containing objects. Inhalation of steam or contact with skin can cause burns that are difficult to heal. The laboratory is generally made of fluorite (the main component is calcium fluoride) and concentrated sulfuric acid, which needs to be sealed in a plastic bottle and stored in a cool place.
-
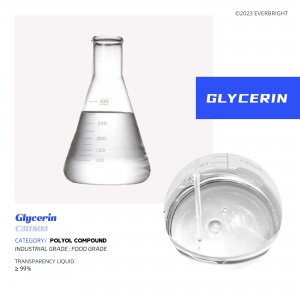
Glycerol
A colorless, odorless, sweet, viscous liquid that is non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids called triglycerides. Because of its antibacterial and antiviral properties, it is widely used in FDA-approved wound and burn treatment. Conversely, it is also used as a bacterial medium. It can be used as an effective marker to measure liver disease. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pharmaceutical formulations. Due to its three hydroxyl groups, glycerol is miscible with water and hygroscopic.
-

Sodium Bisulfate
Sodium bisulphate, also known as sodium acid sulfate, is sodium chloride (salt) and sulfuric acid can react at high temperatures to produce a substance, anhydrous substance has hygroscopic, aqueous solution is acidic. It is a strong electrolyte, completely ionized in the molten state, ionized into sodium ions and bisulfate. Hydrogen sulfate can only self-ionization, ionization equilibrium constant is very small, can not be completely ionized.