-

Sodium Carbonate
Inorganic compound soda ash, but classified as salt, not alkali. Sodium carbonate is a white powder, tasteless and odorless, easily soluble in water, aqueous solution is strongly alkaline, in humid air will absorb moisture clumps, part of the sodium bicarbonate. The preparation of sodium carbonate includes the joint alkali process, the ammonia alkali process, the Lubran process, etc., and it can also be processed and refined by trona.
-

Frangrances
With a variety of specific aromas or aromas, after the aroma process, several or even dozens of spices, according to a certain proportion of the process of blending spices with a certain aroma or flavor and a certain use, mainly used in detergents; Shampoo; Body wash and other products that need to enhance fragrance.
-

Selenium
Selenium conducts electricity and heat. The electrical conductivity changes sharply with the intensity of light and is a photoconductive material. It can react directly with hydrogen and halogen, and react with metal to produce selenide.
-

Acetic acid
It is an organic monic acid, the main component of vinegar. Pure anhydrous acetic acid (glacial acetic acid) is a colorless hygroscopic liquid, its aqueous solution is weakly acidic and corrosive, and it is strongly corrosive to metals.
-

Active Poly Sodium Metasilicate
It is an efficient, instant phosphorus free washing aid and an ideal substitute for 4A zeolite and sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP). Has been widely used in washing powder, detergent, printing and dyeing auxiliaries and textile auxiliaries and other industries.
-

Sodium Alginate
It is a by-product of extracting iodine and mannitol from kelp or sargassum of brown algae. Its molecules are connected by β-D-mannuronic acid (β-D-Mannuronic acid, M) and α-L-guluronic acid (α-l-Guluronic acid, G) according to the (1→4) bond. It is a natural polysaccharide. It has the stability, solubility, viscosity and safety required for pharmaceutical excipients. Sodium alginate has been widely used in food industry and medicine.
-

Formic acid
A colorless liquid with a pungent odor. Formic acid is a weak electrolyte, one of the basic organic chemical raw materials, widely used in pesticides, leather, dyes, medicine and rubber industries. Formic acid can be directly used in fabric processing, tanning leather, textile printing and dyeing and green feed storage, and can also be used as metal surface treatment agent, rubber auxiliary and industrial solvent.
-

Potassium Carbonate
An inorganic substance, dissolved as a white crystalline powder, soluble in water, alkaline in aqueous solution, insoluble in ethanol, acetone, and ether. Strong hygroscopic, exposed to the air can absorb carbon dioxide and water, into potassium bicarbonate.
-
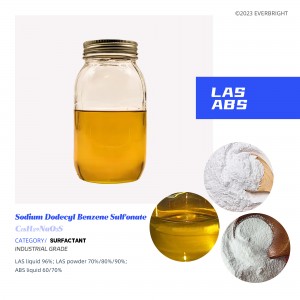
Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate (SDBS/LAS/ABS)
It is a commonly used anionic surfactant, which is a white or light yellow powder/flake solid or brown viscous liquid, difficult to volatilization, easy to dissolve in water, with branched chain structure (ABS) and straight chain structure (LAS), the branched chain structure is small in biodegradability, will cause pollution to the environment, and the straight chain structure is easy to biodegrade, the biodegradability can be greater than 90%, and the degree of environmental pollution is small.
-

Dodecylbenzenesulphonic acid (DBAS/LAS/LABS)
Dodecyl benzene is obtained by condensation of chloroalkyl or α-olefin with benzene. Dodecyl benzene is sulfonated with sulfur trioxide or fuming sulfuric acid. Light yellow to brown viscous liquid, soluble in water, hot when diluted with water. Slightly soluble in benzene, xylene, soluble in methanol, ethanol, propyl alcohol, ether and other organic solvents. It has the functions of emulsification, dispersion and decontamination.
-

Potassium Chloride
An inorganic compound resembling salt in appearance, having a white crystal and an extremely salty, odorless, and nontoxic taste. Soluble in water, ether, glycerol and alkali, slightly soluble in ethanol, but insoluble in anhydrous ethanol, hygroscopic, easy to caking; The solubility in water increases rapidly with the increase of temperature, and often redecomposes with sodium salts to form new potassium salts.
-

Sodium Sulfate
Sodium sulfate is sulfate and sodium ion synthesis of salt, sodium sulfate soluble in water, its solution is mostly neutral, soluble in glycerol but not soluble in ethanol. Inorganic compounds, high purity, fine particles of anhydrous matter called sodium powder. White, odorless, bitter, hygroscopic. The shape is colorless, transparent, large crystals or small granular crystals. Sodium sulfate is easy to absorb water when exposed to air, resulting in sodium sulfate decahydrate, also known as glauborite, which is alkaline.